Embracing one-fifth of the land of our planet and with a share of one-fifth of the world’s population, China is considered to be the most important market of the future in the Asia-Pacific area. lt is on the verge of becoming a newly industrialized country. Since economic liberalization began in 1978, real gross domestic product has grown by an average 6.6% each year.
Jochen Albrecht
China’s economy has been characterized by sharp stop and go cycles. Booms are followed by pronounced phases of consolidation, accompanied by severe austerity measures. These have tended to temporarily dampen growth but should not jeopardize the long term reform process and China’s dynamic economic development. The economic growth forecast 1998 is considered to be about 7.5 to 8.7%
The Chinese economy has undergone profound structural change in the last 20 years. While the share of agriculture in aggregate output has fallen from 42% to 17%, that of the service sector has doubled to almost 25%. But industry has been the major and most dynamic contributor, particularly the increasingly significant manufacturing sector. In view of the immense success of the first special economic zones, the government expanded economic reforms to other regions in the mid-1980s. There has also been progress in the institutional reform. China has encouraged foreign companies to set up businesses, mostly in the form of equity joint ventures, by offering them investment and tax incentives and through exten-sive liberalization measures in the special economic zones. At the same time, it has permitted the establishment of domestic private firms. Between 1986 and 1993, foreign trade rose by an average of about 14% a year and exports by 18%. China is now the world’s tenth largest trader, accounting for over 2% of the world’s trade. China’s foreign trade will most likely continue to grow at rates well above the international average. In 1997 the export exceeded 24% whereas the import increased only by 2.5%. The reasons for this development can be found in the strong foreign and the weak domestic demand as well as in the internationally more competitive private enterprises in China. Many export orientated companies have set up joint ventures with foreign firms. Joint ventures account for roughly one quarter of total merchandise exports.
Given the size of the domestic market and low wages, foreign companies will continue to shift labour-intensive production to China. Formerly China’s economy was dominated by heavy industry. With the introduction of 1978’s economic reforms this situation changed. Light industry quickly expanded and now accounts for about 45% of manufacturing output. Heavy industry is concentrated in central China and the northeast, whereas the manufacturing industry is mainly located along the eastern seaboard.
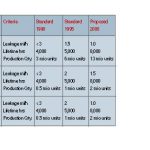
The six major Chinese mechanical seal manufacturers – including the joint ventures – have a market share between 3 and 9% each. There are about 400 so-called “pirates” and small manufacturers with about 40% participation in total. About 26% are imported. The total market potential in 1997 was considered to be about US$ 62m.
Along the coast there are special economic zones with low taxes and low custom duties, independent administration, existing ground and flexible job markets. These include Shenzen, Zhuhai, Shantou, Xiamen, Pudong. Furthermore there are free coastal cities for technical development and export promotion, such as Shanghai, Dairen, Tianjin, Lianyungang, Zhanjiang.
China seals
Most of the seal manufacturers in China are producing mechanical seals for simple applications. A great part of the heavy duty seals have to be imported causing very high import costs. Due to this, China is interested in the local production of these seals with foreign know-how. Incentives are made to attract foreign investors, not only for the transfer of knowledge, but also to be able to increase the export of the local production with high quality seals.
The industry is making efforts in the development of heavy duty seals for large plants mainly for the petrochemical and chemical industry, medium size seals for oil and petrol pumps, seals for corrosion and abrasive media, supply systems, etc. Research and development activities for government projects are being carried out for mechanical seals for nuclear and coal fired power stations, into dry gas seals, seals for the petrochemical industry, seals for solids-containing media, for highly viscous media, for low and high temperatures, into metal bellows seals, corrosion resistant seals and agitator seals for high pressures and large diameters.
China has Environmental Area Managers who have the task of making the environment market more transparent, and of providing information concerning companies, institutions, projects, actual developments, and legislation. The most popular form of cooperation desired in China is an Equity Joint Venture. The lowest permissable participa-tion in the investment by a foreign company is 25%, which then translates to its share in the profit and loss performance. The joint venture company has the right to admit and dismiss personnel. Social insurance and housing costs have to be borne by the company.
Starting up successfully
If a company wants to be successful in China and to start a Chinese business it is necessary to understand the principles and rules, and to adapt to them. This is the result of the influence of the government on the economy. The following points explain how these rules influence the establishment of a joint venture in China:
l lt is easier to penetrate the Chinese market with a Chinese partner.
l The choice of partner will decide the future success of the company.
l Negotiations should take place with several potential partners and the alternatives should be compared thoroughly.
l Get as much as information as possible about the companies and evaluate them systematically.
l Try to find out the motives of the partners for the desired cooperation.
Foreign companies need to be aware of the danger of product imitation, facilitated by ex-company personnel. Strategic plans should also include the fact that besides partners in the product field, partners with a political background should be considered for a joint venture, i.e. ministries, communities or private persons. These partners can be of help with resources and contacts, especially for ground and buildings, personnel, and financial problems. There are about 200,000 companies in China with foreign capital participation. Some of the most important in the chemical industry are: Akzo, Amoco, BASF, Bayer, Ciba, Dow Chemicals, DuPont, ELF Atochem, GE Plastics, Henkel, Hoechst, ICI, Mitsui Sekka, Nestle, Norsk-Hydro, Rhône Poulenc and Roche.
Burgmann involvement in China
The expansion of the mechanical seal market in China encouraged Feodor Burgmann to increase activities there. This has resulted in a licence agreement and the establishment of two joint venture companies, one in Shanghai in 1995 and another in Dalian in 1997 – the complex market and the size of the country required a second joint venture in order to be closer to the different industrial areas. The partners of both joint venture companies are pump and mechanical seal manufacturers who already know the product, the market and the customers. The target with both joint ventures is to cover the whole country by making use of existing sales offices and service centres and by establishing new ones. The production range will be completed with the addition of Burgmann mechanical seal types made according to Burgmann methodology. The joint venture will produce, develop and sell mechanical seals all over the country and export them to the neighbouring countries too. Burgmann Shanghai is a cooperation of Burgmann (51%) and Shanghai Pump Works (49%). It is located in the Minhang Economic and Technological Development Zone in Shanghai and has a very good infrastructure with a high customer potential. The company covers an area of 5000 m2 and employs more than 100 people. Shanghai Pump Works is a state owned company who entered a joint venture with KSB Pump Co in 1994. Burgmann has invested DM 1.8m in this venture. Burgmann Dalian, with 200 employees, is a cooperation of Burgmann (51%) and Dalian Acid Proof Plant (DAPP) (49%), one of the five big pump manufacturers in China and ISO 9000 certified. Burgmann has invested DM 2.3m in this enterprise. Burgmann’s motives for a second joint venture were to
• strengthen its position in China,
• strengthen its global position,
• gain experience with Burgmann Shanghai,
• enhance cooperation with the Dalian plant,
• be part of the fastest growing market of the next 50 years.
After the inauguration of a subsidiary in Thailand end of 97 and Italy beginning of 1998, Burgmann has now 34 subsidiaries worldwide with more than 2,300 employees.
Burgmann
Fax: ++49/8171/23 1095
Further information cpp 235
Unsere Webinar-Empfehlung
Die Websession „Wasserstoff in der Chemie – Anlagen, Komponenten, Dienstleistungen“ (hier als Webcast abrufbar) zeigt technische Lösungen auf, die die Herstellung und Handhabung von Wasserstoff in der chemischen Industrie sicher machen und wirtschaftlich gestalten.
Ob effizienter…
Teilen: